More than a year after hyperinflating banana republic Venezuela stopped reporting official inflation data, Venezuela has stopped publishing money supply data, depriving the general public of the last, and best, available tool to ascertain soaring inflation in what has become the world’s worst-performing economy. Then again, one hardly needs official data to confirm the blistering wave of hyperinflation sweeping through the nation which has seen the value of the bolivar disintegrate under the Maduro regime.
The money supply indicator suddenly stopped appearing on the central bank’s website on Feb. 24. The data in question, which will no longer be updated, looked as follows most recently.

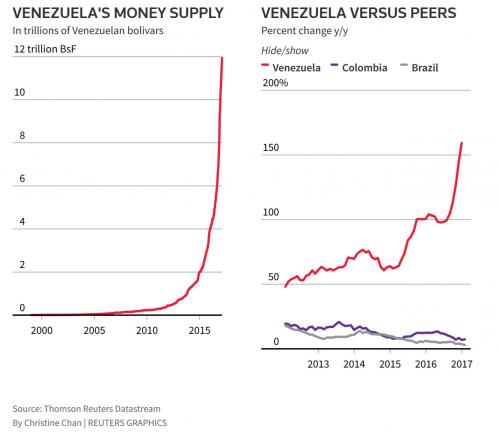
Despite the halt of CPI data, consumer price rises are widely seen to be in triple digits, driven by an unraveling socialist system in which many people struggle to obtain meals and medicines. The M2 money supply was up by nearly 180% in mid-February from a year earlier, according to the central bank before it halted the release of the weekly data without explanation last month Reuters reports. In contrast, Reuters reports that neighboring Colombia’s M2 was up 7 percent in the same period and the United States’ was up 6 percent.
“If they are not publishing, you know it must be skyrocketing,” Aurelio Concheso, director of the Caracas-based business consultancy Aspen Consulting, stated the obvious. The central bank and ministry of communications did not respond to a request for comment, Reuters adds.
An increase in M2, the sum of cash together with checking, savings and other deposits, means more currency is circulating. That can accelerate inflation when coupled with a decline in the output of goods and services – such as in Venezuela, which is in the fourth year of a recession. When money supply is growing exponentially, as it has been in Venezuela, academics usually point to the infamous example of the Weimar Republic and leave it at that.












Leave A Comment