The US is starting to admit that it has a spending problem.
According to the latest Monthly Treasury Statement, in March, the US collected $210.8BN in receipts – consisting of $88BN in individual income tax, $98BN in social security and payroll tax, $5BN in corporate tax and $20BN in other taxes and duties- a drop of 2.7% from the $216.6BN collected last March and a clear reversal from the recent increasing trend…
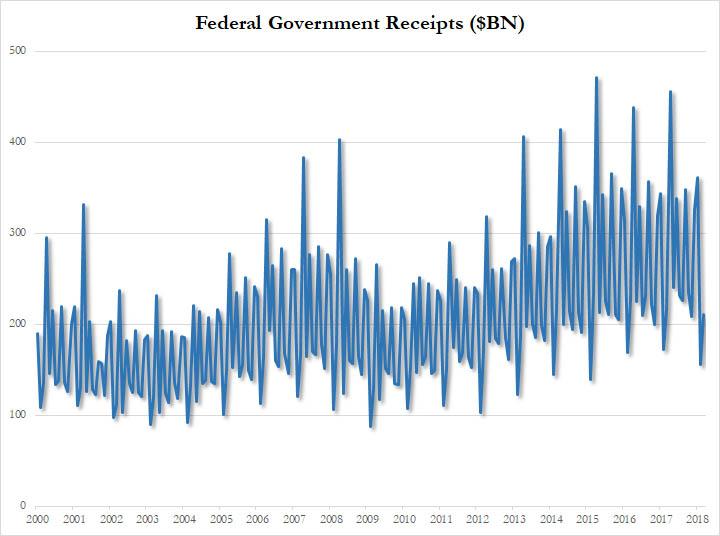
… even as Federal spending surged, rising 7% from $392.8BN last March to $420BN last month, the second highest monthly government outlay on record…
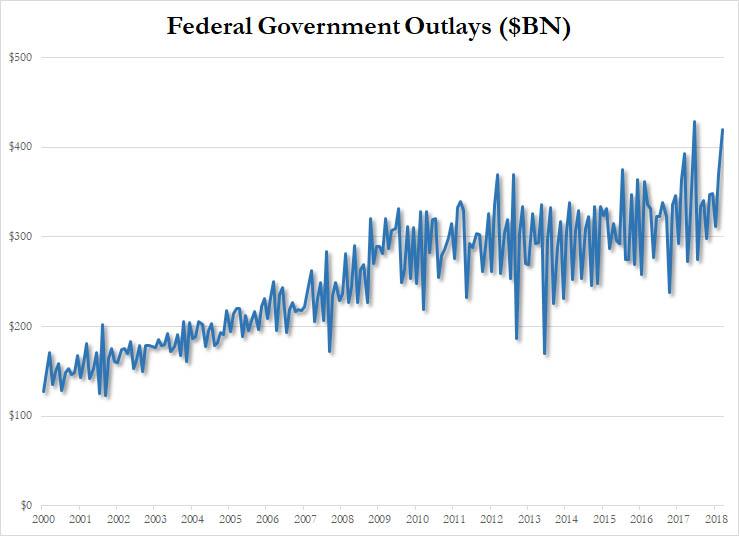
… where the money was spent on social security ($85BN), defense ($58BN), Medicare ($75BN), Interest on Debt ($33BN), and Other ($170BN).
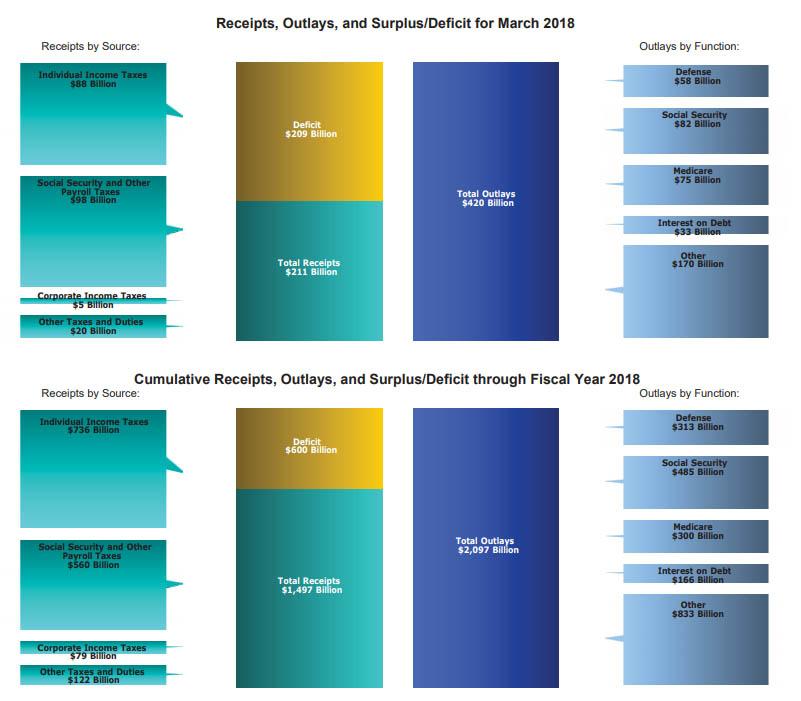
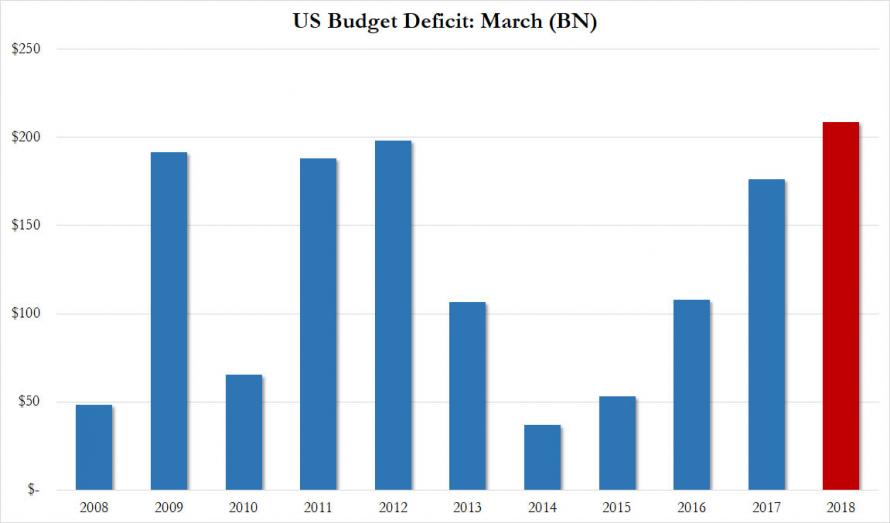
The resulting surge in spending led to a March budget deficit of $208.7 billion, far above the consensus estimate of $186BN, and over 18% higher than $176.2BN deficit recorded a year ago. This was the biggest March budget deficit in US history.
The March deficit brought the cumulative 2018F budget deficit to over $600bn during the first six month of the fiscal year, or roughly $100 billion per month; as a reminder the deficit is expect to rise further amid the tax and spending measures, and rise above $1 trillion, although at the current runrate it is expected to hit $1.2 trillion. As we showed In a recent report, CBO has also significantly raised its deficit projection over the 2018-2028 period.
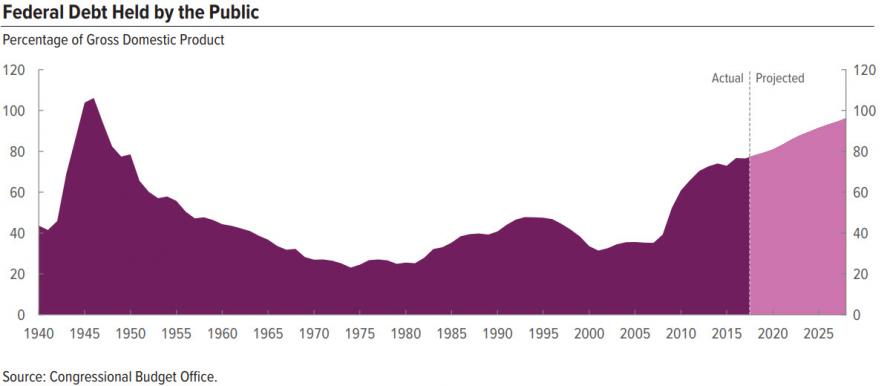
But while out of control government spending is clearly a concern, an even bigger problem is what happens to not only the US debt, which recently surpassed $21 trillion, but to the interest on that debt, in a time of rising interest rates.
As the following chart shows, US government Interest Payments are already rising rapidly, and just hit an all time high in Q4 2017. That’s when Fed Funds was still in the low 1%’s. What happens when it reaches 3% as the Fed’s dot plot suggests it will?









Leave A Comment