(by Wm. Grommen)
Preface from Tim: I received what surely most be Earth’s Longest Post from a reader, who was kind enough to share it here. I’ve broken it up into three parts, each of which is big enough to be seen from space, and I’ll spread these out over three days.
New stock market crash inevitable
Every production phase or society or other human invention goes through a so-called transformation process. Transitions are social transformation processes that cover at least one generation. In this article I will use one such transition to demonstrate the position of our present civilization and and that a new stock market crash is inevitable.
When we consider the characteristics of the phases of a social transformation we may find ourselves at the end of what might be called the third industrial revolution. Transitions are social transformation processes that cover at least one generation (= 25 years). A transition has the following characteristics:
A transition process is not fixed from the start because during the transition processes will adapt to the new situation. A transition is not dogmatic.
Four transition phases
When we consider the characteristics of the phases of a social transformation we may find ourselves at the end of what might be called the third industrial revolution.
The S curve of a transition
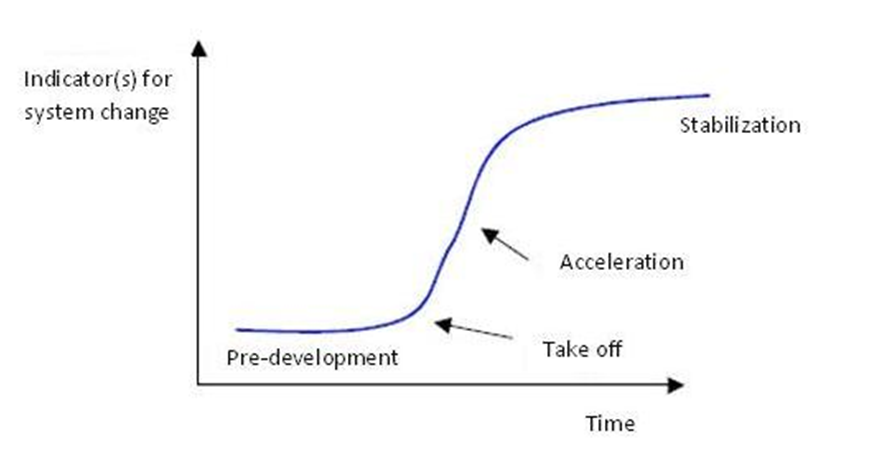
Figure: Four phases in a transition best visualized by means of an S – curve: Pre-development, Take off, Acceleration, Stabilization.
In general, transitions can be seen to go through the S curve and we can distinguish four phases (see fig. 1):













Leave A Comment