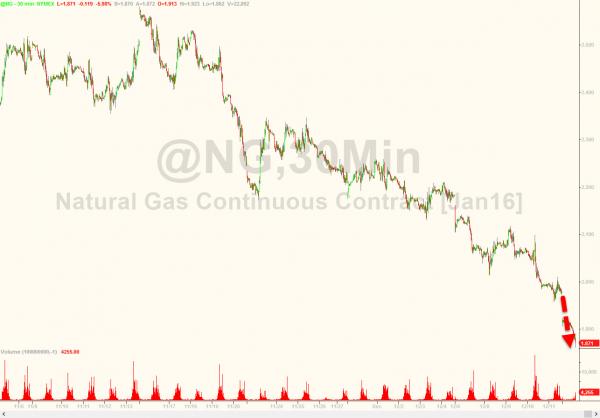
With Nattie down 6% in early trading, the most in 2 months, pressing to new record lows…
OilPrice.com’s Nick Cunningham warns, while the glut in oil is expected to continue for the next year or so before balancing in late 2016, the pain for liquefied natural gas (LNG) could be just beginning…
Building LNG export terminals is a long-term proposition. It can take years to develop a greenfield project, bringing a lump of new capacity online long after the project was initially planned, exposing developers to the possibility that market conditions could change in the interim. It is not unlike a conventional oil project, such as an offshore well, which also can take years (as opposed to a much shorter lead time for shale drilling).
But there is a major difference between oil and LNG: the market for LNG is much smaller and less liquid (no pun intended). In other words, a handful of new LNG export terminals can significantly alter the supply/demand balance.
That is exactly what is currently unfolding. Several years ago, spot prices in Asia for LNG spiked, particularly following Fukushima nuclear meltdown. Japan’s demand for LNG skyrocketed. At the same time, the shale gas revolution was unfolding in the U.S., and rock bottom prices opened up a window of opportunity to ship American gas to Asia. But it wasn’t just the U.S. – LNG export terminals proliferated around the world, particularly in Australia.
There were so many projects planned at the same time, and the first batch started to come online this year, with many more nearing completion in 2016 and 2017.
The rush of new supply is hitting the market all at the same time. Not only would such a rush in supply have pushed down prices on their own, the timing is actually really unfortunate for LNG exporters. Economies in East Asia are slowing, leaving a shortfall in demand. Japan, the largest LNG importer, is seeing its economy stagnate. China’s growth has slowed significantly.








Leave A Comment